Introduction:
When a child, or a teenager under 16, experiences prolonged joint inflammation and stiffness for over six weeks, it may be a sign of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA). This article aims to provide understanding and compassion regarding this condition and its treatment.
Uncovering JRA:
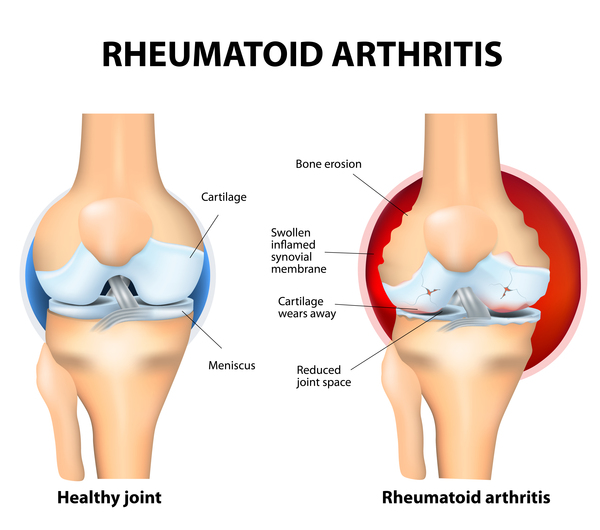
JRA is characterized by inflammation that leads to redness, swelling, warmth, and soreness in the joints. It can affect any joint in the body and may impact joint function. The good news is that with the right treatment, most children with JRA can achieve a full recovery and lead normal lives.
Exploring Various Forms of JRA:
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis presents in different forms:
- Systemic Arthritis: Also known as Still’s Disease, this form can affect the entire body and various systems. It often manifests with high fever and a rash, affecting organs like the heart, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. Boys and girls are equally susceptible.
- Oligoarthritis: This variant affects fewer than five joints within the initial six months. The knee, ankle, and wrist joints are commonly involved, and it may lead to uveitis, primarily in girls. Many children outgrow this condition as they reach adulthood.
- Polyarthritis: Also referred to as polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), it involves five or more joints within the first six months, often affecting the same joints on both sides of the body. This form can also impact jaw, neck, hand, and foot joints, resembling the adult form more closely and being more common in girls.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Occurs in children with both arthritis and the skin disorder psoriasis. Either condition can develop before the other, and children with this type may have pitted fingernails.
- Enthesitis-Related Arthritis: Primarily affects the spine, hips, eyes, and entheses (where tendons attach to bones). This form is more common in boys over 8 years of age and may have a family history of ankylosing spondylitis among male relatives.
Understanding Symptoms:
Symptoms of JRA can vary and may include joint stiffness, pain, swelling, tenderness, limping, persistent fever, rash, weight loss, fatigue, irritability, eye redness or pain, and blurred vision.
Exploring the Causes:
JRA is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks healthy cells, leading to inflammation. It can have genetic, viral, or trigger-based causes.
Diagnosis:
Various tests such as blood tests, X-rays, imaging, and more are employed to diagnose JRA. These tests help differentiate it from other conditions and provide valuable insights.
Treatment and Compassionate Care:
Treatment for JRA combines exercise and medications, tailored to the specific type of JRA and individual needs. The goals of treatment include relieving pain, reducing swelling, improving joint mobility, and preventing complications.
Medications include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and swelling.
- Slow-Acting Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (SAARDs or DMARDs) for long-term management.
- Corticosteroids for pain and swelling.
- Antimetabolites to prevent further joint damage.
- Biologic response modifiers, a newer class of drugs.
Physiotherapy Management:
Physical therapy is crucial in JRA treatment. It focuses on maintaining or improving muscle tone, strength, range of motion, and joint health. Exercises, stretching, and protective measures are key components. Splints or orthotics may be recommended, and stretching exercises help prevent joint contractures.
Promoting Activity:
Children with JRA should remain active and engage in sports when possible. During flare-ups, rest and symptom-reducing therapies are advised. Regular activity and exercise programs help maintain mobility, strength, function, and symptom reduction.
Symptom Reduction:
To alleviate pain and discomfort, various modalities like ultrasound, paraffin wax dips, moist compress, hydrotherapy, and cold packs can be utilized.
In the journey of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis, compassion, understanding, and comprehensive care are essential to ensure children can lead fulfilling lives and manage their condition effectively.